Jigsaw classroom
Jigsaw classroom
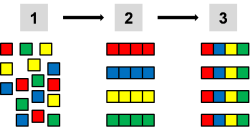
Illustration by Denis Edlich (retrieved on 26.12.2009)
Short description
It is an efficient way for larger groups to learn material using cooperative approach. The group is divided into smaller workgroups, each of 3 up to 6 members maximum. First, each member becomes an expert on specific part of the material (text, questions, problems, or goals) acquiring knowledge about it while working within an expert group. Next, each expert explains their material to other members of their workgroup. Please also watch the introduction video.
Process description
Divide the whole group (class) into 3-, 4-, 5-, or 6-person jigsaw groups (workgroups). The groups should be diverse in terms of gender, ethnicity, race, and ability. Say, we have 4 persons in each basic group: A, B, C, and D.
Divide the lecture topic into corresponding segments (3 up to 6) - see image, left side.
Each member of the workgroup will become an expert for one segment and has to learn it within an expert group.
Form the expert groups (all A's, all B's, all C's, and all D's from each workgroup together) - see image, middle part.
Provide general and specific reference materials (texts, videos, etc.) for each expert group. Let them use books, internet etc. You can inquire how they want to teach their segment to others.
Back in the workgroup, each expert teaches their segment to other workgroup members - see image, right side. Each group should discuss every segment and combine the knowledge from all segments to cover the entire topic.
At the end, the learned material is reviewed (questions and answers, mind mapping, or other methods).
Required resources
Materials appriopriate for each segment (texts, videos, factsheets, etc.). Boards, pens, paper, cards, computers, elearning platform, forums etc. Internet and/or library access.
Examples
Cooperative Learning in different subjects:
Comments
In order to learn the entire material, group members must work well within the expert groups and their workgroups. Since each participant depends on others to learn, there must be a high degree of cooperation and commitment from all participants.
The jigsaw technique was first developed in the early 1970s by Elliot Aronson and his students at the University of Texas and the University of California.
When implementing cooperative learning, it is important that all segments are of similar type and the same level of difficulty.


